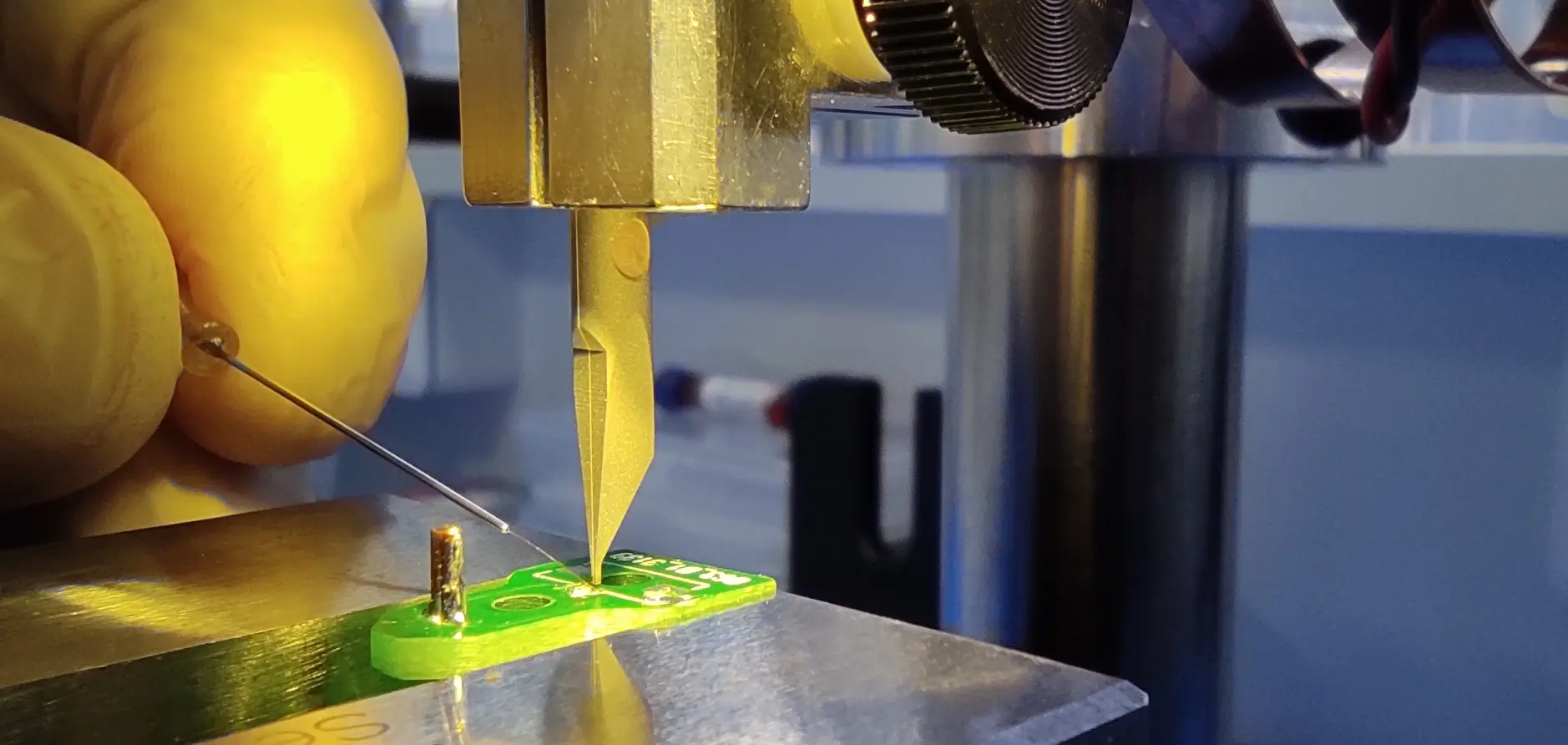
Cisteo MEDICAL is equipped with a second microwelding machine based on resistance welding technology for the manufacture of medical devices.
Why did you choose this resistance welding technology? In order to weld smaller diameters and obtain faster performance, but also to weld different materials, in this case gold on platinum iridium, the alloy used for electrical contacts.
The R&D team thus has an additional process at its disposal when it comes to identifying the most suitable welding technology, particularly for Class III medical devices.
The advantages of resistance welding for medical devices
These machines are currently used for the manufacture of neurological stimulators. For stimulation implants, particularly at the nerve level, we are talking about a diameter of less than 1 mm. Thanks to this technology, Cisteo MEDICAL can weld wires up to 50 microns in a few milliseconds.
Cisteo MEDICAL performs welds on materials that are not necessarily the same, which is a real advantage. Resistance welding allows materials to be combined and provides solutions adapted to miniaturization issues.
For a medical device adapting to the patient's morphology such as the biosensor, spot welding is particularly suitable because it allows the weldability of flexible materials .
This technology offers controllability of the heating temperature and power and in particular allows the welding of pacemaker battery interconnections.
Resistance welding is ideal for medical device manufacturing because the low voltage causes little or no distortion of the materials being joined and produces no contamination .
Thanks to this technology and to make the device innovative, Cisteo MEDICAL designs interconnection options corresponding to the standards of medical devices. Interconnection technologies such as resistance welding make it possible to integrate miniature and compact systems .
How does Cisteo MEDICAL integrate micro resistance welding into its processes?
Implanted devices, which are a real challenge for patients' lives, must benefit from extremely reliable manufacturing processes. This is why the Cisteo MEDICAL R&D team pays particular attention right from the design and prototyping phase in order to guarantee the reliability of the manufacturing process and at the same time the health of the patient and cost control for the manufacturer.
From the development phase of a system, the R&D team integrates the manufacturing method into its thinking and identifies the appropriate welding technique (laser welding, hot bar bonding, resistance welding, ultrasonic bonding).
From one project to another, the technology must be able to adapt to restrictions such as size, geometry, accessibility of the interconnection location.
At Cisteo MEDICAL, our manufacturing engineers may choose to use resistance welding to ensure an interconnection that meets the unique needs of the project but also by extension ensure a durable device that will best fit the patient .
Microsoldering, some technical explanations
As the name suggests, resistance welding uses resistance to current flowing through workpieces to generate welding heat. Like other types of spot welding—such as laser welding—resistance welding is often used in medical device manufacturing because it works well with thin materials.
The choice of welding method to use depends on the materials being welded, the location of the weld, and the desired mechanical strength. Resistance welding works by applying pressure and electricity simultaneously to the areas being joined. Electrodes press the two pieces of metal together, then initiate a low-voltage, high-current DC flow of electricity. The higher resistance felt where the two pieces meet raises the temperature, and the resulting heat causes the metals to bond.
Resistance welding can form a fusion bond where the material on either side of the interface melts, mixes, and solidifies to form a weld. Fusion bonding is quite common for welding resistive alloys such as stainless steels. While the presence of fusion may be considered the preferred type of bond, this is not often the case for medical devices where welding dissimilar metals/alloys is common. In the case of resistance welding, when welding dissimilar metals that have very different melting points, the lower melting point alloy may melt and form a braze on the higher melting point metal.
